Goods and Services Tax – What is GST?
 GST is an indirect tax means that the indirect tax is going to come into effect from 1st July, 2017 in India. And as it is its name, it will look at both goods and services. Nearly 160 countries of the world have already implemented GST.
GST is an indirect tax means that the indirect tax is going to come into effect from 1st July, 2017 in India. And as it is its name, it will look at both goods and services. Nearly 160 countries of the world have already implemented GST.
What does Goods & Services mean?
Goods are those things that we can either use or which can be consumed … can eat and drink. These are the tonsizable things we can touch and see … and can own them. Such as –
- Books
- CDs
- Food and drink items
- Furniture
- Real Estate
- Printers, computers and computer hardware
- Vehicles
- dresses
Services means that we take any kind of service and give money in exchange for it. This is intangible in nature, such as –
- When we cut hair in the parlor, the service tax is included in the bill.
- Even when we eat food in the hotel, we pay service tax.
- Even after making a service of a CA or building a home from an architect, we pay a service tax.
- What happens here is that the service provider who takes money from us for their services, from the same, collects service tax in the government account.
What is this indirect tax?
Two types of taxes are Direct and Indirect. The example of direct tax is income tax paid to a government servant by a jobman.
When we take any luggage, we pay the money according to the MRP written on it. But if we pay attention, then it is written next to the MRP (inclusive of all taxes) i.e. the tax is added to the value that goes to the government. This means we also pay tax in this case but indirectly, so this is a kind of indirect tax.
What is costlier and cheaper after the GST?
See the Image :
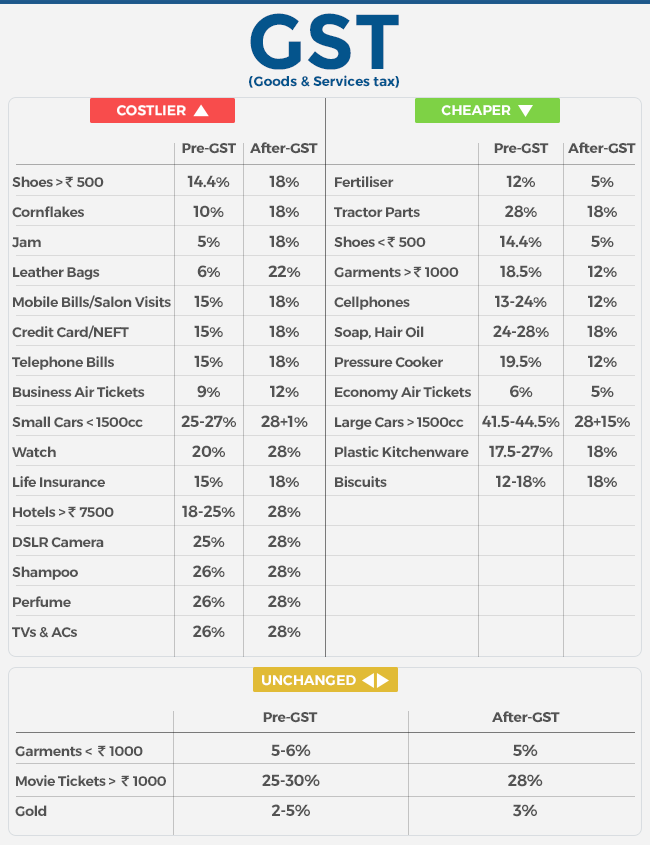
Cheaper and Costlier after GST
Some important things about GST:
GST(Good & Service Tax) is being considered as a major step towards improving India’s indirect tax structure.
GST is a consumption-based tax i.e. means tax will be collected by the state where goods and services will be consumed and not by the state where these goods and services will be manufactured. Different rates and prices will be applicable on different goods and services under GST. Rates of GST have been set.
Basically on all goods and services-
- 0%
- 5%
- 12%
- 18% and
- 28%

GST will be charged at the rate of In particular, rates of 28% on luxury items will apply.
Some things are also that are excluded from the workspace of GST. In such items mainly –
- Five petroleum products such as crude oil, gasoline, diesel, aviation turbine fuel and natural gas etc. are included.
These taxes will disappear after GST
On the implementation of GST, GST will be seen on all goods and services, ie most other indirect taxes will be removed from the tax structure. The list of State Level and Central Level Taxes ended with the arrival of GST is as follows:
State level tax:
- VAT
- Central Sales Tax
- Entry Tax & Octroi
- Entertainment Tax
- Taxes on lottery, betting
- State Cess and Surcharge
Central level tax:
- Service Tax
- Central Excise Duty
- Additional Excise Duty
- Additional Duty of Custom
- Central Cess and Surcharge
Since the right to recover taxes in India is to both the State Government and Central Government, GST has been divided into three parts:
1) State GST
2) Central GST and
3) Integrated GST
- State GST and Central GST will be applicable both in the state (Intra-State) purchase and sale, which will be recovered by the State Government and Central Government in a fixed proportion.
- Inter-state will be engaged in buying and selling between two or more states integrated GST which will be recovered by the Central Government.
Benefits of GST – Benefits of GST in India:
India’s current tax structure is extremely complex. There are many different types of taxes available in India due to tax collection by both the state government and the central government. Due to the presence of Do different, businessmen have to face many difficulties. With the arrival of Goods and Service Tax, these problems will be resolved to a great extent.
The implementation of Goods and Service Tax will benefit both the government and the general public. The purpose behind implementing GST is to earn all these benefits:
1. Ease of doing business –
By the arrival of GST, most of the indirect taxes will be eliminated, due to which businessmen will no longer have to pay different types of taxes nor will they have to face different tax returns. Now all the businessmen will pay only an indirect tax, GST registration and GST, and submit a tax return, GST, as well.
2. End of tax system
At present, Excise Duty and Service Tax are collected by the central government and by the VAT and Sales Tax state government. Due to the reasons given to the central government, the tax to be given to the Central Government (Input Tax Credit) given to the Central Government, on the tax given to the state government and to the state government. Can not be found. Because of which tax is taxed. But after the arrival of GST, due to the end of various types of indirect taxes, the tax on tax will be over.
3. Reduction in tax burden
With the introduction of Goods and Service Tax, most of the indirect taxes of all types will be eliminated and all will have to pay only one tax, GST. Due to these changes, tax burden will come down.
4. Decrease in the value of goods and services
Due to the decline in the indirect tax structure and various types of indirect taxes, tax on goods and services will be lesser than before, which will reduce the value of goods and services.
5. Reduction in tax evasion
Any Vendor input tax credit under GST can be levied only if the person from whom he is buying the goods, pay the tax to his government and sell the goods to the buyer. Pay the invoice. Therefore, this process works in a chain system, which is likely to give a great extent to the current tax evasion.
6. Increase in government tax-income
Both the central and the state government will benefit greatly because of the decrease in tax evasion. Apart from this, improving the indirect tax structure will make the tax structure simpler, which will make more people, and because of this, the tax-income of the government will increase, which can be used for the country’s progress. is.
Any change seems to be painful for our good. Initially there will be problems due to GST, but in the long term, we can get many benefits. Overall, it can be expected that due to the implementation of GST, a positive change on India’s economy can be seen.